Intel held the Intel Internal Foundry Model Investor Webinar on June 21 to explain the shift to a new internal foundry model, where internal product departments and manufacturing departments move to a foundry-like relationship. Industry experts expect TSMC to benefit from Intel's decision.
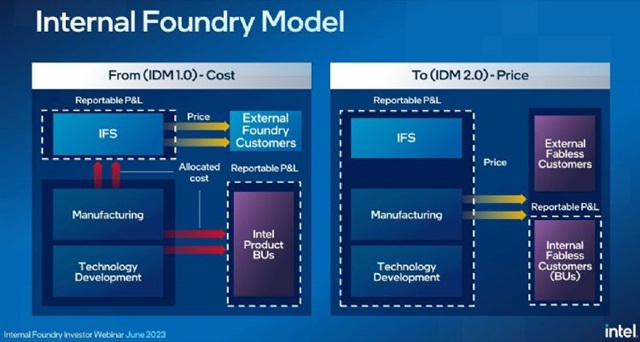
In short, Intel's manufacturing and design divisions are only internal financial cut-offs. From the first quarter of 2024, the profit and loss statements will be presented separately, with the manufacturing division operating independently, but unlike the 2008 split of AMD's manufacturing and R&D design businesses into two, with the manufacturing division drawing in government funding from Abu Dhabi.
Intel said it is now embarking on its most significant business transformation since its inception, regaining process technology leadership through IDM 2.0, expanding its use of third-party foundry capacity, and building a world-class foundry business by significantly expanding its own manufacturing capacity to ensure long-term growth and achieve greater efficiency and cost savings.
Under the new "in-house foundry" model, Intel's product business units will work with Intel's manufacturing division using a similar approach to that of a wafer fabricator and an external foundry.
Intel's internal foundry model is key to the company's overall IDM 2.0 strategy, with the goal of returning its margins to historical ranges and serving its global wafer customers with an expected cost reduction of $3 billion by 2023 and cost savings of $8 to $10 billion by 2025.
Credit: Intel
TSMC to benefit from Intel's expanded outsourcing
The semiconductor industry believes that Intel is expected to become the world's second-largest foundry in 2024. The situation is the same as Samsung Electronics, whose main source of orders and revenue is its own products. In order to enhance long-term competitiveness, to win orders from other chip customers, as well as their own product divisions to reduce the proportion of outsourcing, whether they are willing to place orders with internal foundry is the key.
It is worth noting that Intel has made the design and manufacturing divisions independent of each other, but the manufacturing business is still unprofitable and no external orders have been seen. Intel has not explained how it will support the long-term huge capital expenditure and continue to promote advanced processes, advanced packaging and other technology research and development, which makes outsiders think that this cut between the manufacturing and product divisions is only superficial.
On the other hand, in order to accelerate product launches and boost profits, the next Intel product division is bound to expand the scale of outsourcing. As Intel's manufacturing division and Samsung are both lagging behind in process advancement, coupled with cost, efficiency, and yield considerations, TSMC, which has been taking orders for many years, will benefit the most from Intel's latest move.
Aiming to overtake Samsung and become the second-largest foundry in 2024
Under the new operating model, Intel's manufacturing division will be responsible for its own P&L for the first time. Beginning in the first quarter of 2024, the reported P&L will include the new manufacturing division, comprised of manufacturing, technology development and Intel Foundry Services (IFS), and the product division, comprised of client computing, data center and AI, networking and edge computing, and all other businesses.
Intel's market-driven pricing approach extends to its internal business units, providing them with the same level of certainty and stability as Intel's external customers. Intel will maintain a deep and close relationship between product divisions and technology development teams to continue the strength of IDM.
The new model also drives IFS to build the industry's 2nd largest foundry (based on internal customer order size) in an efficient manner, allowing external customers to leverage Intel's internal scale for development while reducing risk.
Intel's manufacturing division will face the same market dynamics as external foundries and will need to compete for sales volume through performance and price. This also applies to Intel's internal customers, who will have the flexibility to work with third-party foundries as time goes on. But this is not a new concept for Intel; today, about 20% of Intel's wafers are manufactured externally.
Long-term profitability target: 60% gross margin and 40% operating profit
Intel's long-term goals are to achieve a non-GAAP gross margin of 60% and an operating profit of 40%. The in-house foundry model will reveal new opportunities and lead to an optimized cost structure to further achieve these goals.
Intel has previously emphasized its goal of becoming the second largest foundry by 2030, and under the new model, Intel is expected to be the second largest foundry in 2024 with over $20 billion in manufacturing revenue, considering internal order size.
Credit: Intel
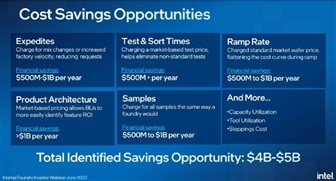
The in-house foundry model will provide a strong incentive for Intel's business units to work more efficiently. For example, a business unit's decision to produce wafers on a "rush" basis through Intel's manufacturing process is very expensive and reduces factory efficiency. In the future, the cost of this service will be borne by the business unit, which is expected to reduce the number of rushes to the same level as the competition.
For example, the cost savings and efficiency gains from reducing rush wafer shipments in the fab are expected to save Intel anywhere from $500 million to $1 billion per year over the long term.
In addition, Intel's test time is currently 2 to 3 times longer than that of its competitors. Since the business unit pays a market price for test time, Intel expects to reduce these test times by making choices in the pre-design phase of the wafer, ultimately saving approximately $500 million per year.
By reducing the number of steps in the wafer process and the number of physical iterations of product design, Intel expects to realize cost savings in the range of $500 million to $1 billion.
In-house Foundry Model: Independent Operations, Service-Oriented Mindset
Intel provides scale and manufacturing advantages to its IFS business by building the second-largest foundry in the world in terms of internal customer order size.
First, by establishing the manufacturing organization as a stand-alone business unit and ensuring that it has decision-making authority to manage profit and loss, Intel will be able to assign clear capacity and supply commitments to external customers.
In addition, because the in-house foundry model is a stand-alone operation that enhances the independence of the manufacturing organization, Intel will provide complete isolation of the data and intellectual property (IP) of its foundry customers.
As part of the shift to an in-house foundry model, Intel is building the service-oriented mentality necessary to gain a foothold in the foundry industry. Intel's manufacturing department and IFS are closely monitoring benchmarking with their peers to ensure that Intel is providing the best possible level of foundry services as expected.
Finally, Intel currently has more than 5 internal products being developed using Intel's latest 18A process technology, and are expected to be available in 2025. This process node will begin with a gradual internal ramp-up to address any potential process issues, which in turn will significantly reduce the risk for external IFS customers.
In addition, allowing manufacturing to operate independently and self-financially, with corresponding transparency and accountability, will be a key driver in achieving Intel's cost reduction target of $8 to $10 billion and long-term profitability goals. Finally, the in-house foundry model will also be a strong driver of the IFS strategy.

Credit: Intel


